Patella Dislocation
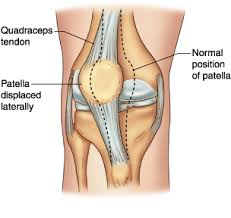
This injury results in the patella (knee cap) moving outside of its natural groove in the joint and dislocating to the outside of the knee. The injury can either be traumatic with a history of trauma, or non-traumatic or spontaneous occurring in individuals whose ligaments are hypermobile.
This injury results in the patella (knee cap) moving outside of its natural groove in the joint and dislocating to the outside of the knee. The injury can either be traumatic with a history of trauma, or non-traumatic or spontaneous occurring in individuals whose ligaments are hypermobile.
What Structures can be Injured?
- Patella and femur joint surfaces
- Medial retinaculum, medial patella-femoral ligament
- Factors that Predispose to Dislocation
- Shape of patella and femoral groove
- Weak connective tissue
- Poor lower limb strength/control
- Poor lower limb biomechanics
Surgical
Surgery is usually only required if there is a history of recurrent dislocation with the role of the surgery to stabilise the patella femoral joint.
Recovery Time
Compliance with your rehabilitation program is essential in achieving a good result following this injury. It can take 3 – 6 months to regain normal function
Treatment
Treatment regime for patella dislocation for the first time will usually consist of a Physiotherapy prescribed and supervised exercise program. If a recurrent dislocation has occurred then a review with an orthopaedic surgeon is advised
- Previous dislocation or history of subluxation
- Age and gender. This is particularly common in teenage girls
Pain and Symptoms
- With the traumatic injuries there is often quite a large effusion (swelling).
- Feeling of something going out of place
- Obvious dislocation of the patella sitting laterally
- Pain
Diagnosis
Often a dislocation can be confirmed with history and clinical examination. An x-ray is usually performed to rule out any fracture or other injury. MRI is frequently used to further assess the knee.
Physiotherapy would usually involve the following:
Activity Modification : To help protect the knee and allow the un-injured tissues of the knee to settle. Appropriate cross training can be implemented to maintain fitness levels.
Exercise – A thorough graded lower limb strengthening program will be developed by your physiotherapist to help restore your full function and assist with return to pre-injury activity. The program should also include a balance and proprioceptive component and finally an injury prevention component.