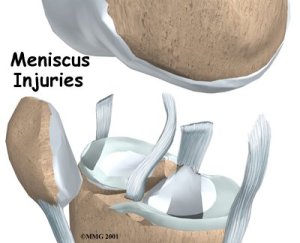
Knee Meniscal Cartilage Injury Part 2
All meniscal tears require a professional assessment and many require a surgical opinion. Central to diagnosis is professional clinical assessment. Further investigations such as x-ray and mri can be used when necessary to exclude other pathologies and to assess the extent of the injury.
Diagnosis
All meniscal tears require a professional assessment and many require a surgical opinion. Central to diagnosis is professional clinical assessment. Further investigations such as X-Ray and MRI can be used when necessary to exclude other pathologies and to assess the extent of the injury.
Treatment
Treatment of a meniscal tear depends on several factors including the type of tear.
Non-Surgical
The blood supply is poor in certain parts of the meniscus and therefore healing is often poor with tears in the avascular zones. If the tear is small and is in the vascular zone there is a greater chance that the meniscus can repair. Also if the tear is only small or if there is only a small amount of degenerative change then a conservative program should be attempted. Treatment would usually include the following:
Physiotherapy.
All patients with meniscal tears should have a Physiotherapy guided rehabilitation plan. The aim of the program will be to restore movement to the knee joint and strength to the surrounding musculature. Balance and sense of position (proprioception) are also affected by this injury and exercises will address any deficiencies with these areas. This will ensure the speediest recovery and will help to minimise complications.
Activity Modification
Aimed at protecting the knee and also allowing the region to settle.
Surgical
With certain types of tears or if the knee has failed to settle with conservative rehabilitation then a review with a specialist would be required. Either a repair of the meniscus would be attempted or trimming of the meniscus would be performed under arthroscope. The next step is then a post-operative rehabilitation program that is controlled by your treating physiotherapist.
Recovery Time
Recovery time for conservative managment is around 6-12 weeks depending on the severity of the tear. Rehabilitation post-operative is around the 8-12 week mark, but once again will be determined by the extent of the tear.
Prevention
Many of these injuries are preventable. Sports people in particular must be taught correct technique in landing and in changing direction. This is the last phase of rehabilitation and these exercises can be integrated easily into the sports person’s training.