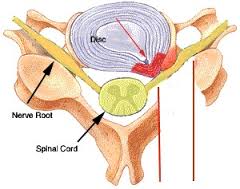
Nerve Root Compression
Nerve Root Compression is a common condition that affects these nerves. It can affect any level of the spine but is more common in the lumbar and cervical spine. The compression is usually the direct result of an acute disc bulge or some bony overgrowth or both leading to a compression of the nerve near these foramina.
Nerve Root Compression is a common condition that affects these nerves. It can affect any level of the spine but is more common in the lumbar and cervical spine. The compression is usually the direct result of an acute disc bulge or some bony overgrowth or both leading to a compression of the nerve near these foramina.
The irritation may be due to the direct mechanical compression of the disc on the nerve or due to the chemical irritation caused by disc.
Causes
- More commonly associated with degenerative change that occurs in the discover time
- Acute disc injury from lifting or twisting movement
- Osteophytes or bony overgrowth
- Spondylolithesis or forward movement of one vertebrae on another
Clinical Features
- Pain is usually severe and will refer down theperipheral limb i.e. leg or arm.
- Can often be associated with weakness, pins and needles, numbness and loss of reflexes.
- Tender over affected region with associated muscle spasm.
- Significant loss of active movements
- Pain is usually aggravated by sitting, bending, lifting and often sneezing.
Diagnosis
MRI or CT scan will help provide a directdiagnosis along with clinical findings. Once thecondition is diagnosed then a decision on the appropriate course of management can be established.
Treatment
Conservative management will usually include:
- Activity Modification – A period of activity modification will be required to help allow the area to settle. Safe activity is important to make sure the spine stays mobile.
- Bracing – A short period of bracing early in the rehabilitation may assist with settling the pain.
- Pain Medication – Early on appropriate pain medication prescribed by your GP may be appropriate in helping to control symptoms.
- Range of Motion Exercises – These are designed to safely restore the active movement in your spine to help with return to functional activities and settle symptoms.
- Strengthening – A strengthening program will be developed to help restore full function, and help with return to daily activities and work.
- Ergonomic and manual handling training – if necessary will be integrated in your program.
A specialist medical opinion is often required and surgery is sometimes necessary.